Drive Layout
Mechanics 2
Understanding how the position of the engine and the drive wheel affects balance
The drive layout refers to where the engine is placed on a car’s chassis and which tires (front or rear) are being driven by the engine. For typical passenger cars, the drive layout can be divided into five categories.
Once you know the drive layout of a car, you know something about its weight-balance tendencies. Cars with better weight balance can utilize all four wheels effectively, which gives a good balance when raising stopping power, acceleration performance and turning performance. The optimal weight balance is 50:50 for both front-to-rear and left-to-right, but the easiest layout in which this can be achieved is the front-engine rear-wheel-drive (FR) layout, where the engine is mounted in the front of the body and the rear wheels are driven.
●FR (Front Engine - Rear Drive)
This is a layout in which the engine is positioned in front of the passenger cabin and the rear wheels are driven. There is a propeller shaft between the engine and rear tires that transfers the drive force. This is the easiest layout in which to achieve an optimal 50:50 weight balance. FR models where the center of gravity of the engine is located behind the front wheel axles are sometimes referred to as ‘front midship’.

FR (Front Engine - Rear Drive)
●FF (Front Engine - Front Drive)
This is a layout in which the engine is positioned in front of the passenger cabin and the front wheels are driven. Because there is no propeller shaft transmitting the drive force to the rear wheels, it is easier to make a roomier passenger cabin. However, because both the heavy engine and the transmission are located at the front, the car is often front-heavy. In addition, because the front tires take on the dual roles of driving the car forward and steering the car, the layout is often unsuitable for high-power machines.

FF (Front Engine - Front Drive)
●MR (Mid Engine - Rear Drive)
This is a layout in which the engine is positioned between the front and rear wheels (often right behind the passenger cabin), and the rear wheels are driven. It is also known as ‘midship’. By placing the heavy engine nearer to the center of the body, it is possible to reduce the yaw moment of inertia and achieve sharp cornering performance. This is a layout that is often utilized in pure sports cars and race cars.
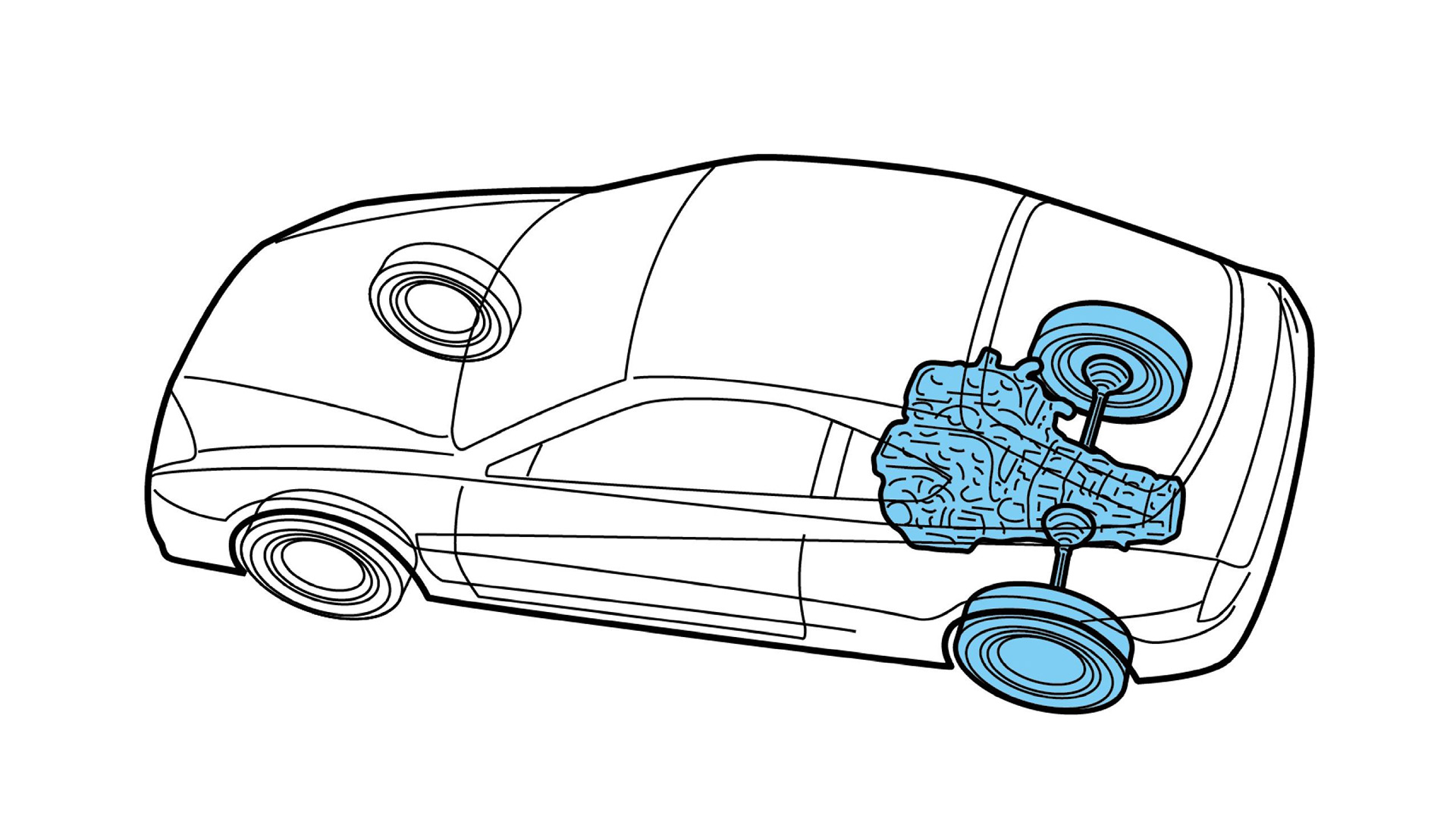
MR (Mid Engine - Rear Drive)
●RR (Rear Engine - Rear Drive)
This is a layout in which the engine is positioned either on the rear wheel axle or overhanging towards the rear, and the rear wheels are driven. This creates an extreme rear-heavy condition, but because the weight of the engine and transmission can be utilized as load on the rear wheels, it makes it easier to gain traction and gives the car good acceleration performance.

RR (Rear Engine - Rear Drive)
●4WD (4-Wheel-Drive)
This is a layout in which engine power is transmitted to all four wheels. Though there is a weight increase due to the mechanism required, this layout gives the best launch and acceleration performance.

4WD (4-Wheel-Drive)
