Types of Suspension
Mechanics 9
Types of suspension and their different characteristics
All suspension types are the same in terms of function: they are intended to maintain a car’s ride height and absorb loads and shocks while driving. However, the performance and characteristics of the different suspension types vary greatly. Below are some examples of leading types of suspension systems.
●Trailing Arm Type
This is a method in which a chassis member crossing the body horizontally is used as an axis, and the arms to which the wheels are mounted are extended out of this towards the rear. The structure is relatively simple and it can be made to weigh relatively little; it does however have little rigidity in the horizontal direction, and can cause the tires to move around horizontally. There are variants known as semi-trailing arms, which are named differently because of the different attachment angles to the axis.
Trailing Arm Type
●MacPherson Strut Type
This is a simple mechanism involving springs, dampers and a lower arm. The “strut” is actually the damper itself, which will serve as the pillar which supports the load. On top of the damper is a part called a mount rubber on which the body is supported, and the bottom of the damper is supported by a knuckle. If fewer parts are used, it can be made light, while it is relatively easy to set a long stroke length (the range in which the suspension compresses and extends) – this has the advantage of making it easier to absorb vibrations from the road surface.
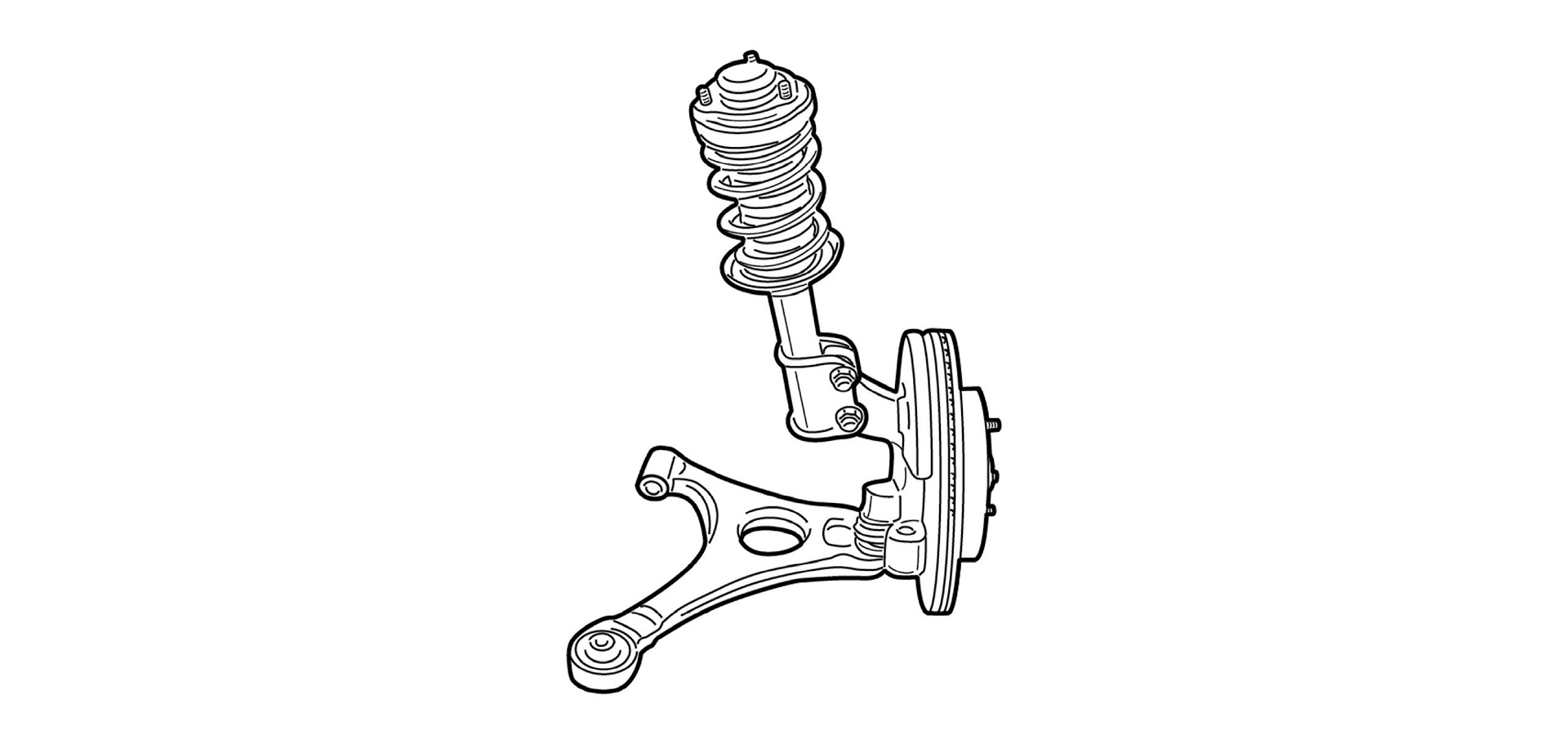
MacPherson Strut Type
●Double Wishbone Type
This is a structure in which a car is suspended by a set of arms on the top and bottom. The name is derived from the two v-shaped arms (shaped like wishbones) at the top and bottom of the suspension. Depending on the arm shape and layout, this format gives good flexibility for controlling the posture and alignment changes of a car during acceleration and deceleration. Because this suspension type is easier to make rigid, it is often used on sports cars which have a focus on control and stability.

Double Wishbone Type
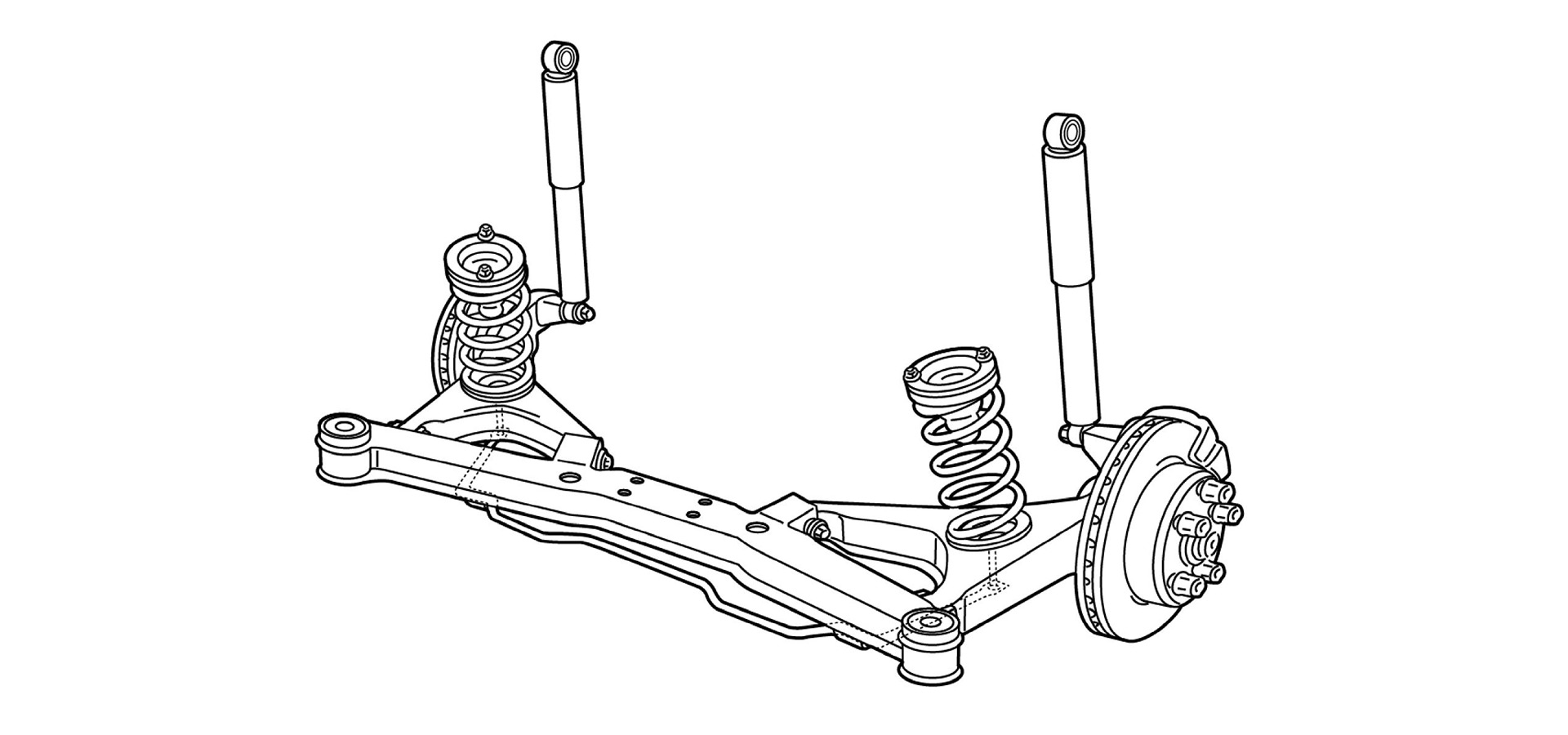
●Multi-link Type
This can be thought of as an advanced version of the double wishbone. While the double wishbone has an arm at the top and one at the bottom, the multi-link type sets the position of the axle with three to five links. Because each arm is independent, there is a great deal of freedom in positioning, which makes more precise settings possible. By supporting the tires with multiple arms, it also becomes possible to precisely control geometry changes in the wheels/tires during the movement of the suspension, in order to achieve superior road-contact performance.

Multi-link Type
